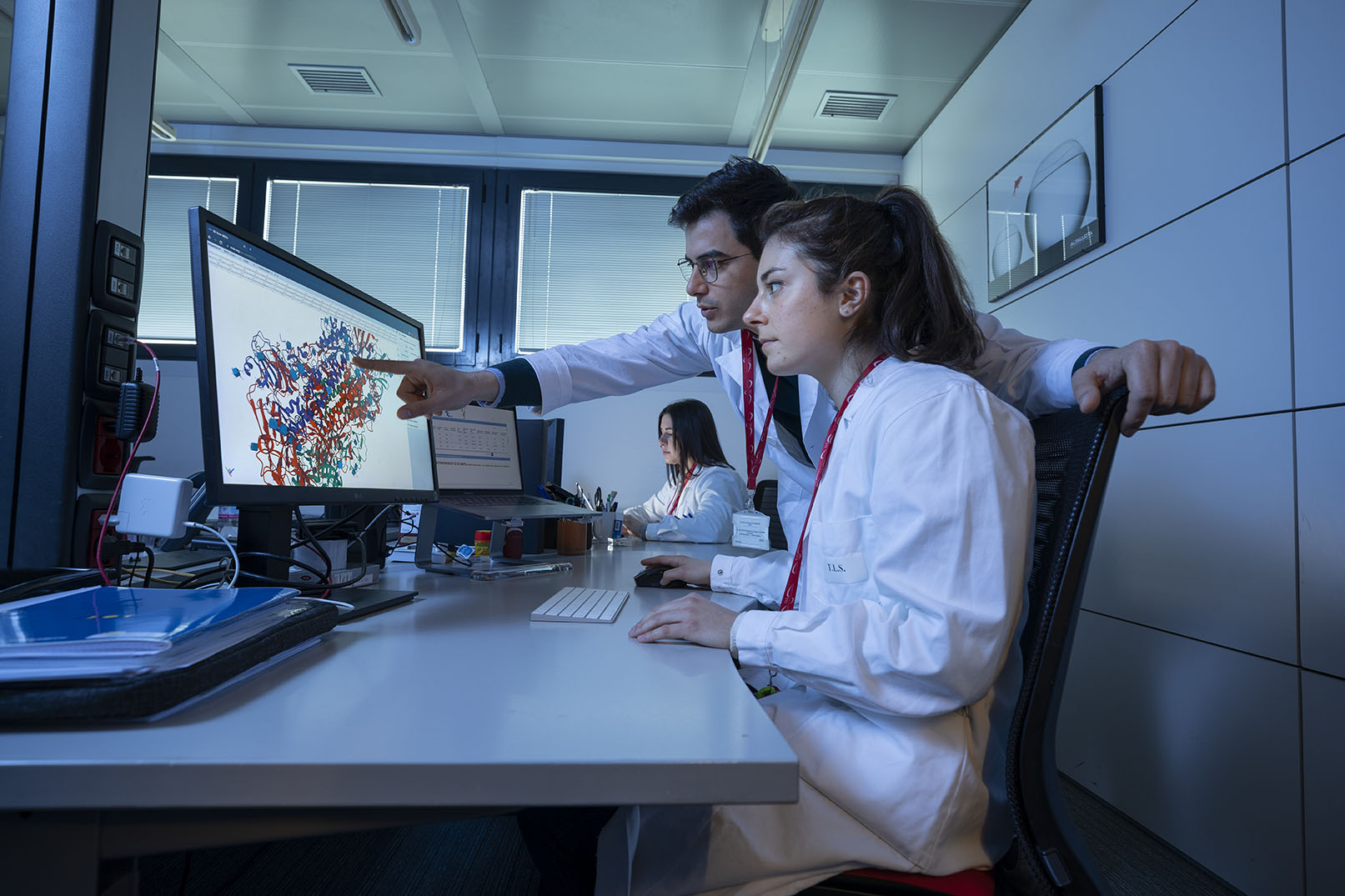
In recent years, the increasing commitment of TLS to in-house research has produced a significant growth of the scientific contribution of the foundation’s researchers

ERC ADVANCED GRANT VAMRES @ MAD LAB
General aspects
This research project aims at producing vaccines able to contrast antibiotic bacterial resistance. The project will last 5 years and represents one of the most important scientific challenges of our time, financed with 2.5 million euros. The project, led by the Principal Investigator Dr. Rino Rappuoli, a pioneer in the field of vaccines, obtained a European Research Council (ERC) Advanced Grant and will be carried out in cooperation with the Fondazione TLS as “host institution”. TLS will provide laboratories, technology platforms and expertise within an innovative and stimulating environment.
Research Activities
Through isolation of natural antibodies and identification of the recognized antigens, “Isolation and screening of human monoclonal antibodies against AMR for therapy and for discovery of novel vaccine antigens” aims at developing vaccines able to defeat Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Gonococcus), Streptococcus pneumoniae (Pneumococcus) and Escherichia coli pathogenic strains. How? By applying advanced technologies to the reverse vaccinology model developed by Rino Rappuoli at the end of the 1990s and now proposed again with a 2.0 approach. Over the last 20 years, the model, based on the completely sequenced genomes of pathogenic bacteria, has enabled the development of vaccines once very difficult to produce. Today, the new high throughput cloning, sequencing, and screening platforms open new opportunities to contrast antimicrobial resistance, a phenomenon that according to the WHO, causes about 700,000 deaths per year, with a forecast for 2050 of more than 10 million deaths, even more than those presently caused by cancer.
Scientific Advisory Board (SAB):
Oretta Finco
Mariagrazia Pizza
Isabel Delany
Aldo Tagliabue
Research Activities
Through isolation of natural antibodies and identification of the recognized antigens, “Isolation and screening of human monoclonal antibodies against AMR for therapy and for discovery of novel vaccine antigens” aims at developing vaccines able to defeat Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Gonococcus), Streptococcus pneumoniae (Pneumococcus) and Escherichia coli pathogenic strains. How? By applying advanced technologies to the reverse vaccinology model developed by Rino Rappuoli at the end of the 1990s and now proposed again with a 2.0 approach. Over the last 20 years, the model, based on the completely sequenced genomes of pathogenic bacteria, has enabled the development of vaccines once very difficult to produce. Today, the new high throughput cloning, sequencing, and screening platforms open new opportunities to contrast antimicrobial resistance, a phenomenon that according to the WHO, causes about 700,000 deaths per year, with a forecast for 2050 of more than 10 million deaths, even more than those presently caused by cancer.